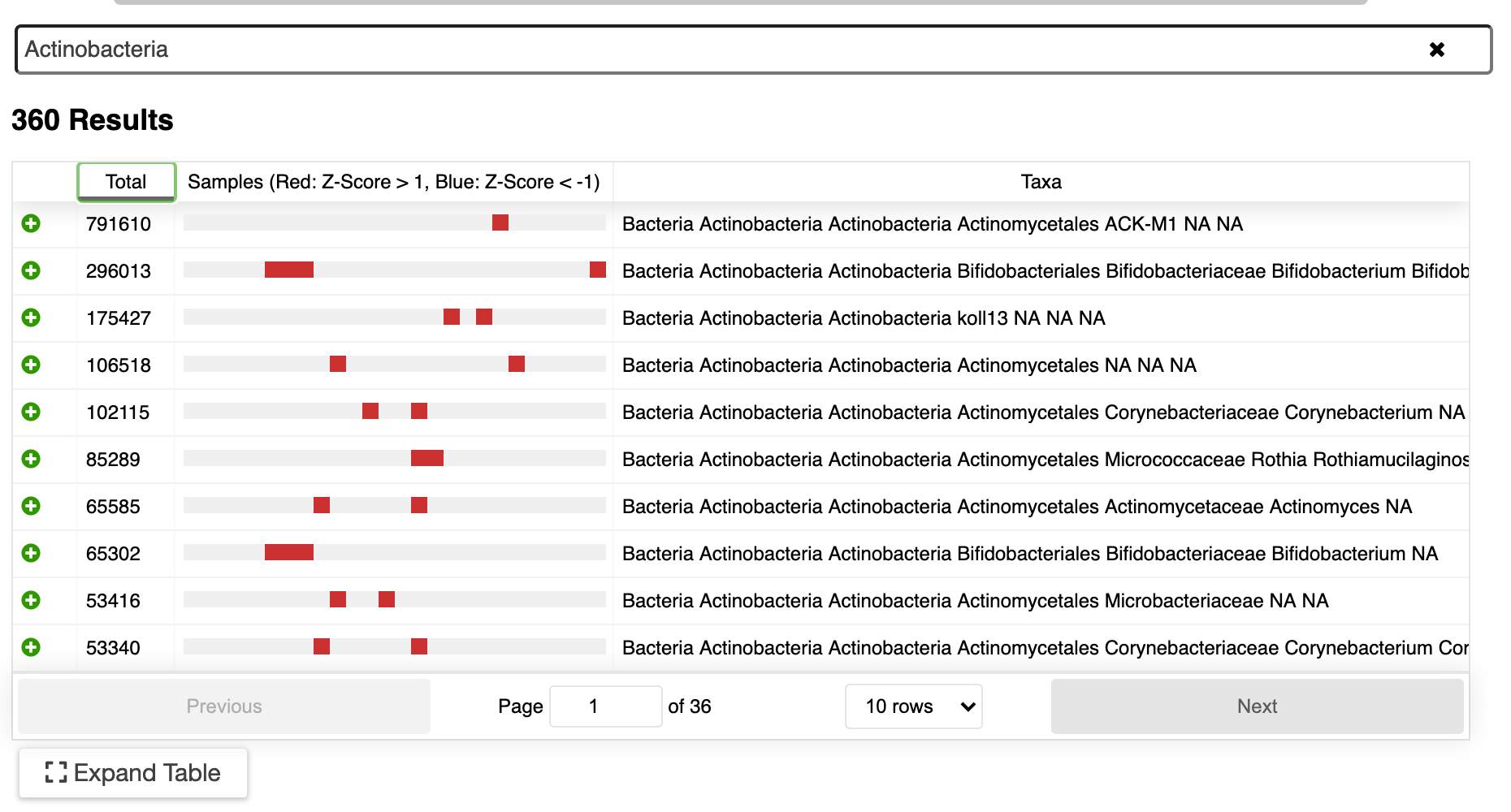
What is 'Denoising' Anway?
/Several different software packages such as DADA2, Deblur, and UNOISE use an error-correction technique that is applied to the sequenced amplicon (usually 16S, 18S, or ITS) reads. This ‘denoising’ step is used to increase correct taxonomic assignment of the sequenced amplicons. DADA2, for example, implements a ‘quality-aware model’ of sequencing errors. This model is then used to ‘correct’ the reads, removing the technical noise of the sequencing methodology but keeping the true biological signal. This differs from the Operational Taxonomic Units (OTU) method in which sequences are clustered to a high but arbitrary similarity threshold (97%, 99%, etc). This threshold is usually picked at a level that can distinguish species.
The Effect of Denoising.
This plot represents the total number of unique sequences identified via UNOISE3, Deblur, DADA2, and classic OTU methods. Notice the reduction in the number of sequences in the denoising methods versus OTU method.
Why ‘Denoise’ at all?
Deniosing techniques help identify true biological differences in the sequencing data, resulting in higher accuracy of the sequence and downstream analysis such as taxonomic assignment, alpha-diversity and others. In the case of DADA2, the resulting Amplicon Sequence Variants (ASVs) are comparable between different runs of DADA2 - unlike OTU techniques which vary significantly depending upon other included sequences. Classic OTU analysis techniques can yield noisy results with significant amount of both false negatives and false positives. This is because one nucleotide could be the difference between identifying very different taxa. One famous example of this is the false identification of Yersinia Pestis on the NYC subway.
There are some instances you may not want to use denoising techniques on your data. For example, your sequencing platform may not be supported. Since ‘denoising’ needs to have information about the expected error rates for a sequencing platform, newer platforms may not be immediately supported.
Integration into ERGO
We’ve integrated dada2 into ERGO2 for the above reasons and more. Running your microbiome analysis could not be easier - just upload the sequences into our cloud platform ERGO and start your analysis.
Want to try ERGO or have other questions about amplicon sequencing? Contact us!
References:
Callahan, B., McMurdie, P., Rosen, M. et al. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat Methods 13, 581–583 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3869
Nearing JT, Douglas GM, Comeau AM, Langille MGI. 2018. Denoising the Denoisers: an independent evaluation of microbiome sequence error-correction approaches. PeerJ 6:e5364 https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.5364